Power To The Edge: Difference between revisions
| Line 66: | Line 66: | ||
[[Image:Developing_Situational_Awareness.jpg]] | [[Image:Developing_Situational_Awareness.jpg]] | ||
LEVELS OF INTEROPERABILITY | LEVELS OF INTEROPERABILITY : | ||
'''''Interoperability can be understood as a spectrum of connectedness that ranges from unconnected, isolated entities to fully interactive, sharing enterprises.''''' | |||
Revision as of 19:28, 21 October 2007
Information Age Transformation Series
Power to the Edge
Command... Control... in the Information Age
David S. Alberts , Richard E. Hayes , with a Foreword by John Stenbit
300 + page pdf
link = http://www.dodccrp.org/files/Alberts_Power.pdf
Related Wikipedia Article Exerpts
Power to the Edge
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Power_to_the_Edge
Power to the Edge refers to the ability of an organization to dynamically synchronize its actions; achieve command and control (C2) agility; and increase the speed of command over a robust, networked grid. The term is most commonly used in relation to military organizations, but it can equally be used in a civilian context.
"Power to the Edge" is an information and organization management philosophy first articulated by the U.S. Department of Defense in a publication by Dr. David S. Alberts and Richard E. Hayes in 2003 titled: "Power to the Edge: Command...Control...in the Information Age." This book was published by the Command and Control Research Program and can be downloaded from the Program's website.
Network-centric warfare
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Network-centric_warfare
Power To The Edge's radical ideas had been under investigation by the Pentagon since at least 2001. In UIAW, the concept of peer-to-peer activity combined with more traditional hierarchical flow of data in the network had been introduced. Shortly thereafter, the Pentagon began investing in peer-to-peer research, telling software engineers at a November, 2001 peer-to-peer conference that there were advantages to be gained in the redundancy and robustness of a peer-to-peer network topology on the battlefield. Colonel Robert Wardell said "You have to empower the fringes if you are going to... be able to make decisions faster than the bad guy".[3]
Network-centric warfare/operations is a cornerstone of the ongoing transformation effort at the Department of Defense initiated by former Secretary of Defense Donald Rumsfeld. It is also one of the five goals of the Office of Force Transformation, Office of the Secretary of Defense.
Excerpted Graphs
Power to the Edge
http://www.dodccrp.org/files/Alberts_Power.pdf
Portions of this publication may be quoted or reprinted without further permission, with credit to the DoD Command and Control Research Program, Washington, D.C. Courtesy copies of reviews would be appreciated.
Interoperability
page 138
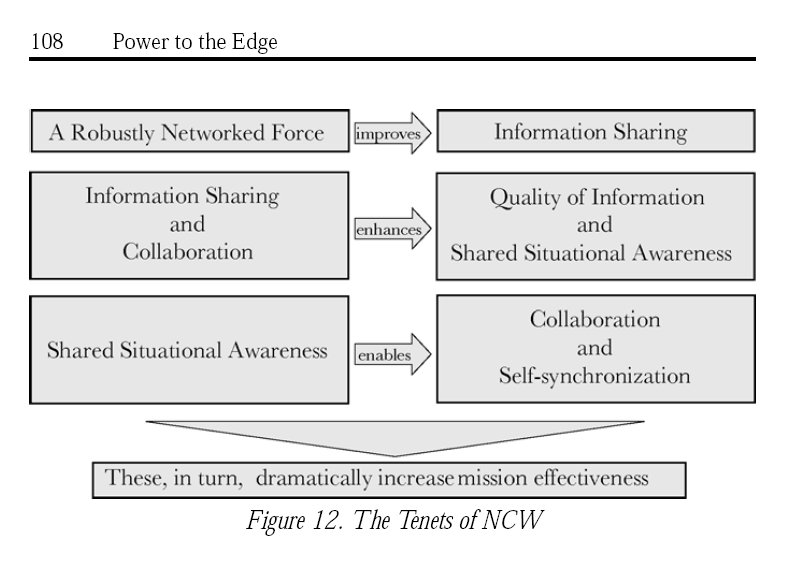
Interoperability, the ability to work together, needs to simultaneously occur at a number of levels to enable entities to communicate, share information, and collaborate with one another.
The degree to which forces are interoperable directly affects their ability to conduct network-centric operations.
Interoperability must be present in each of the four domains: physical, information, cognitive, and social.
Developing Situational Awareness
page 139
LEVELS OF INTEROPERABILITY :
Interoperability can be understood as a spectrum of connectedness that ranges from unconnected, isolated entities to fully interactive, sharing enterprises.